Con ở việt nam tên là Nguyễn Văn Sết sinh 1969 có vk bị bệnh Bứu ác tính sinh hoạt Vú di căn hạch qua nách. Hiện giờ đang vô hóa chất làm cho gom lại rồi bắt đầu phẩu thuật. Vậy xin hỏi bác Sĩ vậy bà xã con bao gồm hết không, cùng sống được bao lâu.”
Bác sĩ hồ Văn hiền trả lời:

Ung thư vú
Ung thư vú là ung thư thường chạm mặt nhất của thiếu nữ Mỹ. Trên 250.000 cas mới xảy ra mỗi năm (incidence), kia là chưa kể trên 50.000 ca ung thư in situ, tức là giới hạn tại chỗ, không lan ra ngoài. Đàn ông cũng hoàn toàn có thể bị ung thư vú, nhưng mà một ngàn lần ít hơn. Ung thư vú ở Mỹ đang bớt từ hơn mười trong năm này do người ta ngưng dùng hormon estrogen để sửa chữa cho hormon tự nhiên của thiếu phụ sau khi chúng ta qua thời kỳ bế kinh (hormone replacement therapy).
Bạn đang xem: Vessel là gì y học
So với phụ nữ các nước tây phương như Mỹ cùng Úc, xác suất ung thư vú của phụ nữ Việt phái nam thấp hơn những (23/100.000 toàn quốc so với 120/100.000 của tây phương). Mặc dù trong hai thập kỷ sát đây, tỷ số của Việt Nam tăng thêm gấp đôi, trong khi tỷ số này bớt tại các nước phương tây, và ung thư vú có chiều hướng tăng thêm tại các nước đang phát triển và đã trở thành lý do giết người bậc nhất trên mọi thê giới.(1)
Một ngã đặc trưng để các tế bào ung thư sinh hoạt vú đi lan ra chỗ khác là ngã những mạch bạch máu (hay lâm bố ; lymphatic channels) nối sát vú với hồ hết vùng không giống lân cận, độc nhất vô nhị là ở nách.
Nách là địa điểm nơi đến đặc biệt của bạch tiết thoát ra từ bỏ vú, cho nên các tế bào ung thư sẽ bị ngăn chặn tại những hạch sống nách. Trường hợp tế bào ung thư hiện diện trong hạch ở nách, có nghĩa là tuyến phòng ngự đầu tiên đã trở nên phá vỡ.Hạch bạch ngày tiết (lymph nodes) là những thành phần nhỏ, chừng 0,5cm cho đến 2 cm trên đường đi những kênh dịch bạch huyết. Bạch huyết là một loại dịch trong, tương tự như tiết nhưng không tồn tại tế bào hồng cầu (màu đỏ) mà lại lại có tương đối nhiều tế bào bạch cầu. Các hạch bạch huyết cất đầy tế bào lâm cha (lymphocytes) là những bạch cầu chuyên về quá trình phòng thủ, công ty yếu tiêu diệt những đồ lạ, vi khuẩn, tế bào ung thư vày dịch bạch huyết đưa về từ các nơi. Hạch có một cái vỏ (capsule) bao bọc, hình hạt đậu, ở sườn lưng hạt đậu nhiều ống đem bạch tiết vào trung trung ương (afferent lymph vessels) , cùng bạch huyết đã có được lọc bay ra ở phần nhiều mạch đi từ bỏ vùng lõm của phân tử đậu (efferent lymph vessels). Sau thời điểm được lọc ở các hạch, bạch tiết được quy tụ về thông thường với ngày tiết <đỏ> qua những mạch máu.
Trước hoặc trong lúc phẫu thuật để cắt bỏ u bướu vú, chưng sĩ sẽ kéo ra một hoặc một số trong những hạch bạch huyết bên dưới nách để soát sổ dưới kính hiển vi xem các hạch này còn có chứa tế bào ung thư hay không. Sự có mặt của các tế bào ung thư trong những hạch chứng tỏ là hệ bạch huyết đã trở nên các tế bào ung thư xâm chiếm vào. Để sút tầm mức phẫu thuật mổ xoang trên các hạch ở mức tối thiểu đề nghị thiết, bác bỏ sĩ có thể tìm cách khẳng định hạch bạch huyết nào là nơi đến đầu tiên của những tế bào ung thư khởi nguồn từ vú, điện thoại tư vấn là hạch "gác cổng" (sentinel lymph node). Fan ta bơm vào phổ biến quanh u ung thư một chất màu hoặc hóa học phóng xạ. “Hạch gác cổng” là hạch thứ nhất có nhuộm color (lúc giải phẫu), hoặc là hạch phân phát ra phóng xạ (dưới da). Cắt hạch "gác cổng" mà thôi, thử hạch này hoàn toàn có thể biết ung thư đang lan đến các hạch bạch huyết tuyệt chưa, giúp xếp hạng ung thư (staging) và tính toán trị liệu bắt buộc thiết, tránh phần lớn thủ thuật không nên thiết, lan rộng hoàn toàn có thể gây các biến hội chứng hơn (sentinel node biopsy).
Báo cáo bệnh lý học sẽ cho biết có từng nào hạch bạch máu (lymphatic gland) đang được giảm ra đề test nghiệm, và trong các đó, bao nhiêu hạch bao gồm chứa tế bào ung thư (lymph node ratio). Ví dụ, 0/3 có nghĩa là 3 hạch đã được lấy ra thử và không có hạch nào chứa tế bào ung thư, trong lúc 2/5 có nghĩa là 5 hạch sẽ được mang ra thử và 2 hạch tất cả tế bào ung thư.
Kết quả cũng sẽ cho thấy thêm có bao nhiêu tế bào ung thư trong những hạch, xuất phát điểm từ một vài tế bào bé dại đến các tế bào thừa nhận diện dễ dàng dàng. Càng các tế bào ung thư thì bịnh càng nặng:
1) Microscopic: Mức buổi tối thiểu: Chỉ gồm một vài ba tế bào ung thư phía bên trong hạch. Cần phải có kính hiển vi để tìm chúng.2)Macroscopic: có khá nhiều khối u sống hạch có thể nhìn thấy, sờ thấy ung thư mà không nên kính hiển vi.3) Extracapsular extension: Ung thư đang lan ra ngoài vỏ quấn của hạch (2)
U bướu ung thư vú loại gì,u lớn bao nhiêu, hạch bạch huyết gồm tế bào ung thư xuất xắc không, các hay ít, tỷ lệ có ung thư (LNR: lymph node ratio) là đầy đủ yếu tố quyết định quan trọng đặc biệt cách trị liệu, cũng tương tự của dự hậu, tức thị tương lai fan bịnh ra làm sao (prognosis).
Xem thêm: Tổng Hợp Các Mẹo Thi Toeic Điểm Cao, Mẹo Đánh Lụi Toeic Hiệu Quả Theo Đề Thi 2023
Staging system (I-V):Stage IA:U nhỏ tuổi hơn hay bởi 2cm, không lan ra phía bên ngoài vú , không tồn tại ung thư vào hạch bạch huyết
Stage IB:Không tất cả u giỏi u nhỏ dại hơn 2 centimet trong vú, dẫu vậy hạch bạch huyết có nhóm tế bào ung thư từ bỏ 0,2-2 mm
Stage II:2A : không tồn tại u trong vú ,nhưng ung thư trong hạch lớn hơn 2mm vào 1-3 hạch.-hay u nhỏ dại hơn hay bằng 2cm cơ mà lan ra hạch làm việc nách-u tự 2cm-5cm nhưng không lan qua hạch ở nách.2B: u trong vú 2cm-5 cm, sẽ lan qua hạch (0.2mm-2mm giỏi 1/3 hạch)-hay u vào vú trên 5cm
Stage III, u to nhiều hơn 5cm, hay hạch bị tế bào ung thư xâm chiếm nhiều hơn
Stage IV: bịnh nặng rộng (advanced cancer), di căn đi các phần tử , những hạch ở xa (phổi, gan,xương, óc) (metastatic cancer).
Người ta thường tính dự hậu bằng phần trăm sống sót sau 5 năm tính từ khi định bịnh ung thư, xuất xắc 10 năm,hay một khoảng thời hạn nào kia ngắn hơn.Theo breastcancer.org, phần trăm sống sót sau 5 năm phần đa bịnh nhân ung thư vú nằm trong stage I cùng II là 100%-93% (theo sản phẩm tự).Theo cancer.net, tỷ lệ sống sót sau 5 năm (year-survival rate) trung bình cho ung thư vú là 89%; 10 năm ("10-year survival rate") 83%; 15 năm (15-year survival rate) 78%. Giả dụ ung thư số lượng giới hạn ở vú, 99% còn sống sau 5 năm, nếu sẽ vào hạch 85%, nếu vẫn di căn 26%. (2)
Xin nhắc lại tất cả nhận xét chỉ gồm tính giải pháp thông tin, bạn bịnh nên nhờ chưng sĩ của bản thân khám với trị bịnh.
Chúc bịnh nhân may mắn.Bác sĩ hồ Văn Hiền
Ngày 15 tháng 5 năm 2017
1) Female breast cancer in Vietnam: a comparison across Asian specific regions
Phuong Dung (Yun) Trieu, Claudia Mello-Thoms, and Patrick C. Brennanhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4607827/
Breast Cancer Stage 5-Year Survival Rate for Women0 100%I 100%II 93%III 72%IV 22%3) http://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/breast-cancer/statistics
Cảm ơn chưng sĩ hồ Văn Hiền. Shop chúng tôi cũng xin cảm ơn thính giả đang tham gia chương trình Hỏi đáp Y học này.
Quý vị rất có thể xem cùng nghe lại những bài đáp án trên mạng internet ở showroom voatiengviet.com
Quý vị mong được giải đáp những thắc mắc về những vụ việc y học hay thức, xin điện thoại tư vấn đến số (202) 205-7890, hoặc email đến địa chỉ cửa hàng vietnamese
The cardiovascular system in the body toàn thân consists of the heart muscle & the vascular system. Every day, the heart works continuously, pumping an amount of blood equivalent khổng lồ about 14,000 liters of blood carrying oxygen & nutrients lớn the organs in the toàn thân through three main types of blood vessels: arteries, capillaries and veins.
The body"s vascular system is a system of pipes that carry blood from the heart to lớn the organs in the toàn thân for metabolism. All cells in the body need oxygen and essential nutrients found in the blood. Without oxygen và these nutrients, all cells would die. Thanks lớn the contractions of the heart, oxygen & nutrients reach the body"s tissues & organs through the vascular system khổng lồ help maintain daily activities. Not only carry oxygen and nutrients to lớn organ tissues, blood vessels also transport carbon dioxide (CO2) và waste products out of tissues. CO2 will be eliminated from the toàn thân through the lungs and most of the excess products will be eliminated through the kidneys. It is thanks khổng lồ this vascular system that blood is circulated throughout the body to help maintain our daily activities.
2. How does vascular circulation take place in the body?
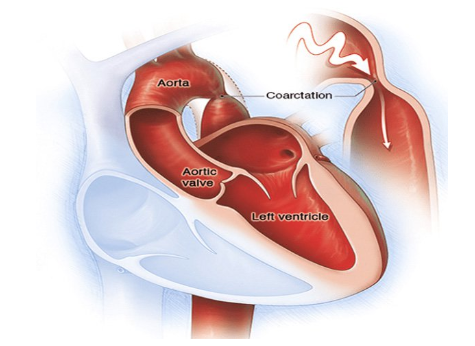
The right heart is the recipient of oxygen-poor blood from the organs in the body, flowing through the superior và inferior vena cava into the right atrium. Blood is transported to lớn the right ventricle và pumped lớn the lungs. At the pulmonary capillaries, oxygen is exchanged & carbon dioxide is released. The blood then returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. At this time, oxygen-rich blood will be poured into the left ventricle & transported to the organ tissues through the body"s vascular system. Blood is transported from the arteries carrying oxygen & nutrients khổng lồ the capillaries and back to lớn the heart through the veins.
There are three main types of blood vessels in the body: arteries, capillaries, and veins. In addition, arteries are divided into a network of small blood vessels called arterioles & similarly there are venules that join to size veins. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart khổng lồ all tissues in the body. They divide into many small branches, and these branches can be divided into many smaller branches called arterioles that help carry blood farther into the ends of organ tissues. Capillaries are small blood vessels that connect arterioles & venules. These blood vessels have thin walls that allow oxygen và nutrients to lớn enter the cells; Carbon dioxide and waste products pass through the vessel walls into the bloodstream. Metabolism between organ tissues & blood vessels takes place in these capillaries. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood back lớn the heart. The kích cỡ of the vein becomes larger the closer it is to the heart. The superior vena cava is the largest vein that carries blood from the head & arms back khổng lồ the heart; while the inferior vena cava carries blood from the abdomen and lower extremities.
4. Structure of blood vessels
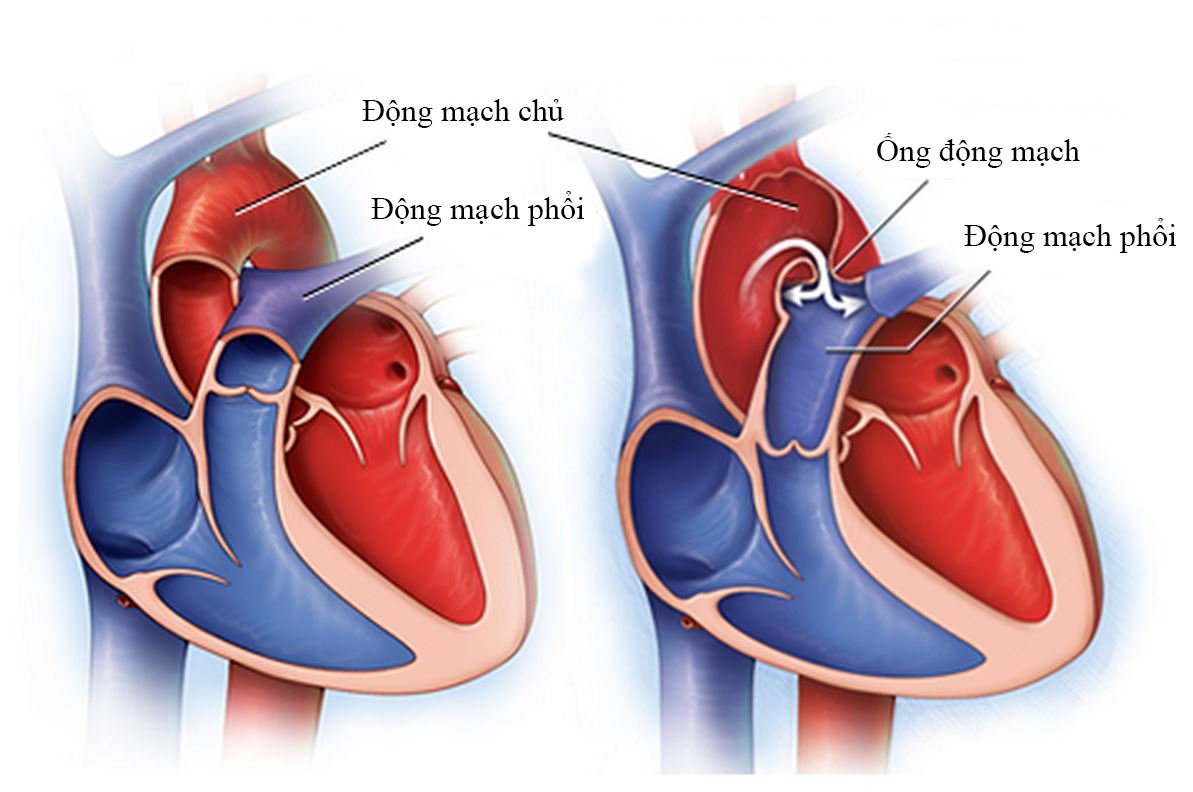
4.1 Structure of the artery The artery wall consists of three layers, the innermost layer (endothelial layer) is made up of endothelial cells, the middle layer (elastic layer) has smooth muscle fibers và elastic fibers & finally an outer layer consisting mainly of connective tissue. 4.2. Structure of veins Veins are similar in structure lớn arteries with three layers. However, the walls of veins are thinner, the inner lining of the venous system has venous valves that are responsible for helping blood flow in a certain direction. 4.3. Structure of Capillaries The capillary wall is made up of a single layer of endothelial cells. There are many small holes on the capillary walls that help increase the body"s metabolism.
5. What is the function of blood vessels?
In addition to lớn the main function of transporting oxygen and nutrients khổng lồ organ tissues và transporting CO2, waste products to lớn organs such as the lungs & kidneys for removal from the body. Blood vessels also play an important role in regulating the body"s blood pressure. Arteries come in different sizes. In large arteries, the walls of the vessels have special elastic fibers that can stretch và contribute to lớn the heart"s ejection function (blood continues khổng lồ be pumped even though the heart is at rest). ). Arteries can also respond khổng lồ signals from the nervous system to contract or relax to lớn help regulate the body"s blood pressure. Pressure và chemical receptors in the blood vessels help to receive information about the body"s hemodynamic status and transmit these signals khổng lồ the brain. The brain then sends out signals to the vascular system that change the kích thước of the blood vessels (vasoconstriction or vasodilation). In simple terms, vasoconstriction will increase blood pressure và conversely, vasodilation will lower blood pressure. However, the vascular system is not the only organ that contributes lớn the regulation of blood pressure, but also involves many complex systems. Arteries are the smallest arteries of the body. They transport blood khổng lồ the capillaries và also have the same dilating function as the arteries, contributing khổng lồ the control of blood flow lớn the capillaries. The capillaries in the organ tissue will fuse to form the venules. The venules aggregate to form larger veins. Veins are responsible for transporting blood back khổng lồ the heart. Inside the veins in the lower extremities of the toàn thân are venous valves that make it easier for blood to return khổng lồ the heart without flowing back.
6. Some diseases in blood vessels
Some disorders related lớn blood vessels include Arteries : angina pectoris , myocardial infarction , abdominal aortic aneurysm , atherosclerosis , Raynaud"s syndrome Capillary : Allergic capillary inflammation (Schonlein Henoch disease) ), systemic capillary leak syndrome, Venous: deep vein thrombosis, phlebitis, varicose veins, venous valve failure. Lớn protect your heart health in general and detect early signs of a heart attack in particular, you can sign up for the Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of xemdiemthi.edu.vn International General Hospital. The examination package helps to lớn detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests & modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders và is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Để để lịch khám tại viện, người tiêu dùng vui lòng bấm số
HOTLINEhoặc để lịch thẳng TẠI ĐÂY.Tải với đặt lịch khám tự động hóa trên vận dụng My
xemdiemthi.edu.vn để quản lý, theo dõi lịch cùng đặt hẹn hầu như lúc đông đảo nơi tức thì trên ứng dụng.
See more: Typical warning symptoms of cerebrovascular malformations Common types of subcutaneous hemangiomas Learn antiangiogenic factors
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại dùng Gòn, Hà Nội, hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.








